How To Find The Period From A Graph
Sinusoidal functions(TRIGONOMETRY)
Trig functions similar sine and cosine have periodic graphs which we called Sinusoidal Graph , or Sine wave .
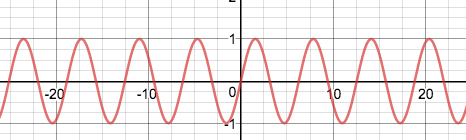
Every menstruation of sine moving ridge is a whole unit of measurement circle:
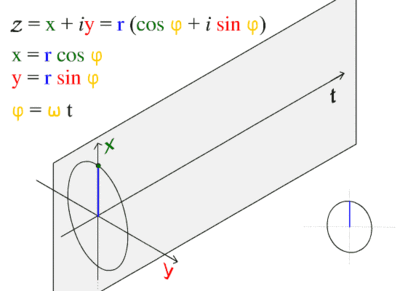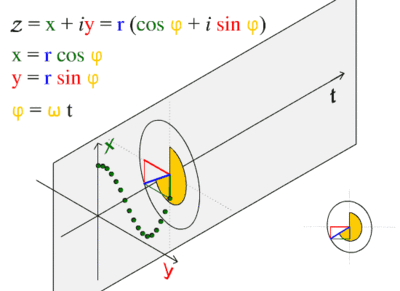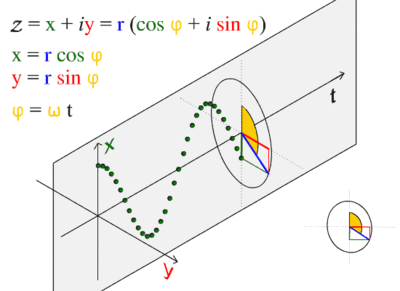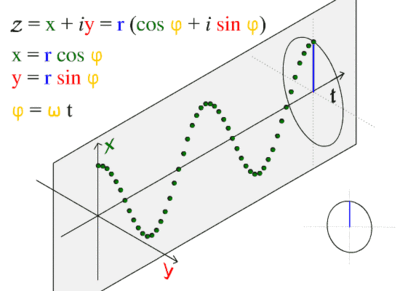
Sinusoidal graphs
Math is fun: Graphs of Sine, Cosine and Tangent.
Symbolab example.%2B10)
Graph of unit sine & cosine function:
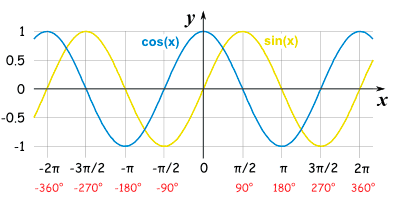
Midline, amplitude and catamenia
They're three features of
sinusoidal graphs.
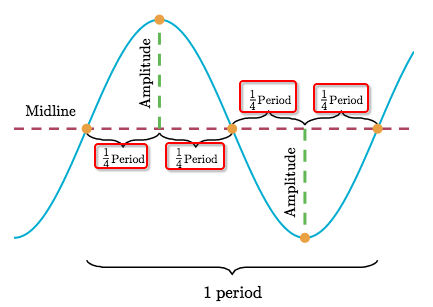
-
Midline: is the horizontal line that passes exactly in the middle between the graph'due south maximum and minimum points. -
Aamplitude: is the vertical altitude between the midline and 1 of the extremum points. -
Menstruum: Also calledfrequency, is the altitude betwixt two consecutive maximum points, or ii consecutive minimum points (these distances must be equal).
Initial period and how to graph a sinusoidal function
To graph the whole function, you only need i period of the graph, and and so only repeat that ever and ever.
And to avoid any defoliation, nosotros'd pick theinitial catamenia, which:
-
sin(ten)that interval is [0,2π], and looks like anSouthward. Y-intersect at its midline. -
cos(x)that interval is [0,2π], and looks like aBow. Y-intersect at its peak.
You actually need to pay attention for the starting indicate of the S and the bow, it's the great way to effigy out the how much the graph shifted on 10-axis.
The necessary information to draw the initial period :
- Any two of the 3 position: Max, Min and Midline
- Menstruum
- Stage shift from
initial betoken
With these information above, nosotros could figure out all other informations almost the menstruum.
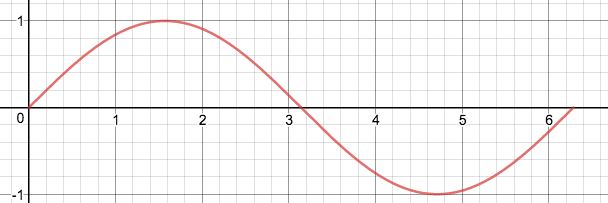
Initial flow of sin(x):
Looks like a
flipped S.
Starting signal of the flipped S is its Midpoint , at (0,0),
Full period is 2π, Midline at y=0, Range is [1,-1].
Initial period of cos(x):
Looks similar a
bow.
Starting point of the bow is its Acme , at (0,1),
Full period is 2π, Midline at y=0, Range is [1,-ane].
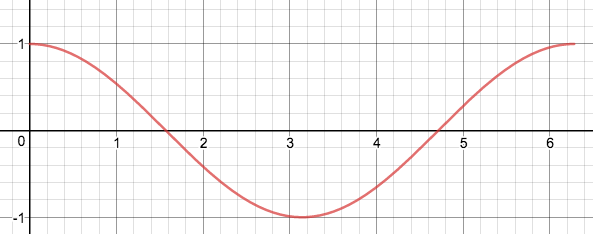
Stage shift of trig functions
Phase shiftmeans horizontal shift, or moves on x-centrality. It's much harder to sympathise and summate than the vertical shift.
Since trig functions(sine, cosine, tangent) are all periodic functions, and so it'southward really Disruptive with horizontal moving, because it's repeating, and you tin't easily tell what happened with the graph.
Calculate algebraically how much is the Phase Shift
First demand to figure out the starting point of the initial menstruation, and to compare how much it moved from 0 on x-axis.
Youtube tutorial: How do you determine the phase shifts for sine and cosine graphs
Youtube tutorial : Sine Role Phase Shift
Since the initial period of both sine and cosine functions starts from 0 on ten-axis,
with the formula of function y = A*sin(Bx+C)+D,
we are to set the
(Bx+c) = 0, and solve forx,
the value of x is the stage shift of the graph.
Why practice nosotros set (Bx+c) = 0?
Because nosotros could imagine the (Bx+c) is a whole, and could be w of the sin(due west).
Since the initial flow of sin(westward), always starts from 0,
we could say the starting point of initial period is 0, so west=0, then Bx+C=0.
Peak points (Max & Min)
Let's phone call the
INITIAL PEAKS, which is thepeaksof theinitial period.
Y-axis position of ALL peaks could be institute in the office'south Range , which could also exist express as [Max, Min] or [Min, Max].
Y-axis position of Initial peaks:[-1, one]
or
Y-axis position of all peaks:
- Max:
y= Midline_position + Amplitude - Min:
y = Midline_position - Aamplitude
Refer to the step-by-step solution at Symbolab.%3D2sin%5Cleft(2x%2B3%5Cright)%2B5)
Ten-axis position of Initial peaks:
- sin(x):
- Max:
x=π/2 - Min:
10=3π/two - cos(x):
- Max:
x=0 - Min:
ten=π
To go the x position of these acme points, need to consider the Phase shifteffect:
- Whatever in the
sin(...), merely assume it is standard functionsin(u). - Match the
x positionof standard role, east.g.sin(u)is at Max whenu=π/2. - Solve the equation of
uto getx position, due east.g.sin(2x+3), set2x+three = π/2to getx. -
10is thex positionof the peak point of theinitial period.
How to find pinnacle points of any period
The Y-centrality position of peak points are maintaining THE Same as the flow repeats.
The X-axis position of meridian points of the number north menses is:
Initial_peak + n*(Period_length) Instance:
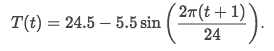
Observe the value of t when it'south at the office's everyman bespeak.
Solve:
-
Max pointof-sin(u)is theMin point. - X-position of the function at Initial Period is
u=π/2 - Solve the equation
u=π/twoto gett:
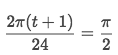
Informations of Sinusoidal functions
For the Full general sinusoidal part:
f(x) = A・sin(Bx + C) + D -
Amplitude: |A| -
Period: |2π / B| -
Vertical shift: D -
Midline: y=D -
Range: [-A+D, A+D] -
Phase shift: Set up(Bx+C)=0, and solve forx. -
Sign of function: is the Same sign of the slope of the ORIGINAL function's Y-intersect signal.
Case:
f(10) = - 2sin(2x + 3) + 10 - Amplitude: |-2| = 2
- Catamenia: |2π / 2| = π
- Vertical shift: +10
- Midline: y=ten
- Range:
[2+10, -two+ten]= [12, 8] - Horizontal shift: set
2x+3=0, becomex=-3/ii, and then it's shifting-3/2from origin.
Example 2:

Solve:
- Midline:
y=2.v - Amplitude:
|6-ii.5|=3.5 - Period: Midpoint to Max is 1/4 catamenia, so
1/four * 2π/B = |-4π - (-5/2)π|, solve for B gets1/3. - Phase shift:
-4π. Considering themidpointon the left is thestarting bespeak of initial period
At this moment, our formula is about finished:
y = 3.v*sin(1/3 *x +C) +2.5, so only the C is not yet solved.
set one/three *x + C = 0, since , since -4π is the phase shift, then nosotros set ten=-4π, solve C gets 4π/3.
Source: https://medium.com/all-math-before-college/sinusoidal-functions-trigonometry-91d49128f9af
Posted by: stewartrefspot.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find The Period From A Graph"
Post a Comment