How To Find Gcf Using Distributive Property
Use the distributive holding to express a sum of two whole numbers 1–100 with a common factor as a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers with no mutual cistron.
For example, express 36 + 8 as 4 (ix + two).
Common Core: 6.NS.4
Suggested Learning Targets
- I can find the greatest common factor and least common multiple.
- I can use the distributive property for whole numbers with no common cistron.
- I tin apply the Distributive Holding to rewrite addition issues by factoring out the Greatest Common Cistron.
Component Skills from Previous Grades
| 3.OA.5 Utilise backdrop of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. For example, write 8 × 7 every bit eight × (five + 2) = (8 × five) + (8 × 2) = twoscore + sixteen = 56. (Distributive property.) | GCF & LCM Find the greatest mutual factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least mutual multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. |
The post-obit diagram shows how to use the GCF and Distributive Property to find the sum of two numbers. Coil down the page for more than examples and solutions on GCF and distributive property.
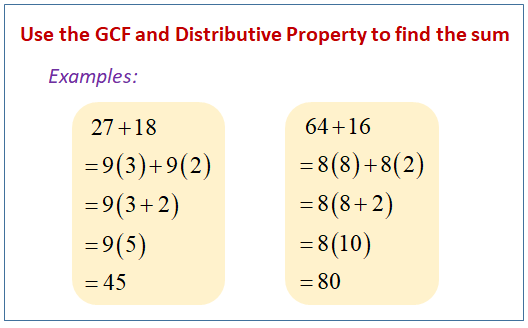
Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
How to find GCF
GCF and Distributive Belongings
6NS4 - Distributive Belongings
Example:
3(2 + 6)
- Show Video Lesson
6NS4 - Multiple of a Sum
How to write a sum of two whole numbers equally a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers?
- Show Video Lesson
GCF and Distributive Property
Case:
Use the GCF and the distributive belongings to express a sum equally a production.
xx + 35
- Show Video Lesson
Example:
Use the GCF and the Distributive Property to express the sum equally a product
xviii + 27
- Prove Video Lesson
GCF and the Distributive Property
Step ane: Find the GCF of the ii numbers
Footstep 2: Re-write using the distributive property.
Case:
Use the GCF and the Distributive Property to limited the sum.
36 + viii
27 + 18
25 + sixty
Instance:
Apply the distributive property to the algebraic expression.
24x + 18y
10x + 15
16x + 32y
- Show Video Lesson
GCF And Distributive Property Word Problems
Learn how to apply solve bug using the GCF and Distributive Holding
Example:
Bryan is setting chairs for a graduation ceremony. He has 50 blackness chairs and 60 white chairs. Each row volition have the same number of chairs and and each row will have the same color chair.
What is the greatest number of chairs that he tin can fit in each row?
How many rows of each color chair will there be?
- Show Video Lesson
Apply the GCF and Distributive Property to solve word problems
Instance:
A shop clerk is bagging spices. He has 18 teaspoons of cinnamon and xxx teaspoons of nutmeg. Each bag need to contain the aforementioned number of teaspoons and each purse can contain only one spice.
How many teaspoons of spice should the clerk put in each purse?
How many numberless of each spice would there exist?
- Show Video Lesson
GCF and Distributive Property Problem Solving
Learn how to use the GCF in problem solving. Distinguish how to use the distributive holding in problem solving.
Example:
Madison has 56 roses and 42 daisies to employ in floral centerpieces for a party. Each centerpiece will have the aforementioned number of flowers and will contain merely roses or only daisies.
What is the greatest number of flowers that Madison tin utilize in each centerpiece?
- Bear witness Video Lesson
Try the free Mathway estimator and problem solver below to do various math topics. Endeavour the given examples, or blazon in your own problem and check your answer with the stride-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
Source: https://www.onlinemathlearning.com/gcf-distributive-6ns4.html
Posted by: stewartrefspot.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Gcf Using Distributive Property"
Post a Comment